Mosquito Joe explores the fascinating world of female mosquitoes.
|
As much as we all hate mosquitoes for their itchy bites that can spread disease, did you know that the real culprits are just female mosquitoes? It’s true — male mosquitoes get a bad rap. Only female mosquitoes are the blood-thirsty pests that spoil backyard barbecues and camping trips because only female mosquitoes bite. Why female mosquitoes bite and how this relates to female mosquitoes’ size and lifespan is an intriguing story. Read on as the bug pros at Mosquito Joe® tell the story and provide additional cool info about female mosquitoes. You’ll even learn how you can avoid becoming their next snack.
Why Do Female Mosquitoes Bite?
The reason why female mosquitoes bite is to consume a blood meal so they can lay their eggs — hatching out the next generation of blood-suckers. They require the proteins available in mammalian blood to produce their eggs. Female mosquitoes bite animals and humans to get a blood meal after mating with a male. They can bite within just two days of reaching their adult stage. Their flagella (antennae hairs) help them find the mammals they can feed on. They also have special receptors for detecting heat, sweat, and carbon dioxide (CO2) in exhalations, which help direct female mosquitoes to the next blood meal.
Male mosquitoes don’t drink blood at all. They enjoy an entirely vegetarian diet of pollen, nectar, and juices from rotting fruit. The female mosquito actually does the same—until she mates. The act of mating triggers her need for a blood meal. The blood, in turn, triggers and supports her egg production.
The thought that the female mosquito is using your blood to produce more mosquitoes is worse than the itchy bite itself!
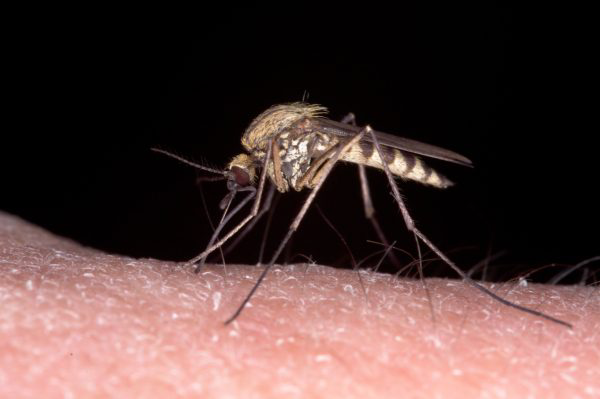
How to Identify a Female Mosquito
Since only female mosquitoes bite, we need to know how to identify a female mosquito, right? One difference between male and female mosquitoes is size. Females are typically 10 - 20% larger than males, and they swell with their blood meals. When a female mosquito has a blood meal, her stomach expands and can hold up to three times her body weight in blood (yuck!).
Female mosquitoes are larger, but males appear bushier due to the fine hairs, called flagella, on their antennae. Males use their flagella to home in on the females’ wing beats, which are pitched a bit higher than males’, aiding their search for a mate. The female’s less bushy antennae contain the odor receptors that help her detect a blood host.
While both male and female mosquitoes have a proboscis, which is a pointed mouth part, only the female proboscis is barbed and strong enough to pierce an animal’s skin to suck blood. Females are aggressive, seeking out animals and humans for blood. On the contrary, males actively avoid any human contact. A male mosquito’s primary interest is finding a mate.
Despite these physical differences between male and female mosquitoes, the easiest way to identify female mosquitoes is by their behavior. The mosquito that bites you is female!
Female Mosquito Lifespan and Reproduction
Depending on the mosquito species, females typically live longer than the males. The lifespan of female mosquitoes ranges from several weeks to five months, depending upon environmental factors, including temperature, humidity, and the availability of food and hosts. In colder climates, some female mosquitoes enter a dormant state called diapause to survive the winter cold and resume activity when spring’s warmth returns. Meanwhile, male mosquitoes live fast and die young, typically within 6 - 10 days.
The lifespan of female mosquitoes is longer than males’ because they are busy. After mating with up to six females, the male’s biological purpose is finished, but the female’s is just getting started. Female mosquitoes mate just once. The mating triggers the female’s search for a blood meal, which in turn stimulates her to begin developing and laying her eggs. Laying eggs triggers another search for more blood, which stimulates the laying of more eggs. A female mosquito actually stores the male’s sperm, doling it out to successive batches of eggs she lays every few days.
Each batch of eggs the female mosquito lays contains 100 to 200 eggs and is preceded by a blood meal. While females typically lay 3 to 5 egg batches in their lifespan, they may lay ten or more times in favorable conditions. She seeks out standing water to lay her eggs where her larvae can develop. Birdbaths, ponds, puddles, and any stagnant water caught in odd containers are favorite breeding grounds. Female mosquitoes can lay up to three hundred eggs in just a bottle cap full of water! This is why eliminating sources of standing water on your property is essential when combatting mosquitoes.
Are Female Mosquitoes More Dangerous?
Mosquitoes are considered the most dangerous animals worldwide due to the many deadly and damaging diseases they spread to humans and animals. When female mosquitoes bite to take a blood meal, they inject their saliva into the wound to numb the bitee and prevent clotting so they can suck more blood. If the person they bite has a disease like Zika, malaria, or dengue fever, the female ingests the disease pathogens right along with the blood. Within a few days, the biter becomes infected and is able to spread the disease. When the female mosquito bites the next person for a blood meal, they will inject the infectious pathogens along with their numbing and anti-clotting saliva. (Ick!)
Since only female mosquitoes bite, it’s certainly fair to say that female mosquitoes are far more dangerous than males. Of course, both male and female mosquitoes are required to perpetuate the species. However, the unique behaviors of the females can be exploited by ingenious mosquito traps that selectively target, trap, and eliminate females. These traps effectively target and control female mosquitoes, clearing the property of these biting pests.
How to Protect Yourself from Female Mosquitoes
There are several strategies you can use to protect yourself from getting bitten by female mosquitoes:
- Use Insect Repellant: Use EPA-approved repellants containing DEET, picaridin, or essential oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed skin and clothing.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves and pants to avoid bites. Learn what clothing mosquitoes cannot bite through.
- Repair Window and Door Screens: Keep the nasty biters outside where they belong!
- Eliminate Standing Water: Empty all containers, plant catch trays, bird baths, and other objects that collect water. These are prime mosquito breeding sites.
- Run Fans: Mosquitoes are weak flyers. Sitting in a fan’s draft keeps female mosquitoes from being able to reach you to bite.
- Hire Professional Mosquito Control: For long-term, effective solutions like mosquito misting systems or barrier treatments, call the mosquito control experts at Mosquito Joe.
Staying Safe from Female Mosquitoes
Trust the pros at Mosquito Joe to protect you and your family from female mosquitoes. Our comprehensive pest control services include several options we can customize to your specific needs and property to get rid of your mosquito problem. We’re confident you’ll be pleased with our service because we back it with the Neighborly Done Right Promise® and our own Satisfaction Guarantee!
Ready to enjoy your backyard in bite-free bliss? Request your free estimate, and we’ll take care of the rest!
